Web3 protocols are the cornerstone of the emerging decentralised internet, often called Web3. These protocols are of paramount importance as they lay the groundwork for a new generation of decentralised, interoperable, and user-centric applications and services. Unlike traditional Web2 protocols, which rely on centralised servers and intermediaries, Web3 protocols operate on peer-to-peer networks, enabling direct user interaction. They are designed to facilitate various activities, including data storage and retrieval, digital transactions, and smart contract execution, all securely and transparently.
In essence, Web3 protocols are the rules and standards that govern how nodes in a decentralised network communicate and interact, thereby enabling the shift from a centralised to a decentralised web. Understanding these protocols is critical to grasp the potential and promise of Web3, as they form the backbone of this new, decentralised version of the internet.
Blogpost Contents
ToggleThe Evolution of the Web
The evolution of the web has been a transformative journey, reshaping how we interact with information and each other.
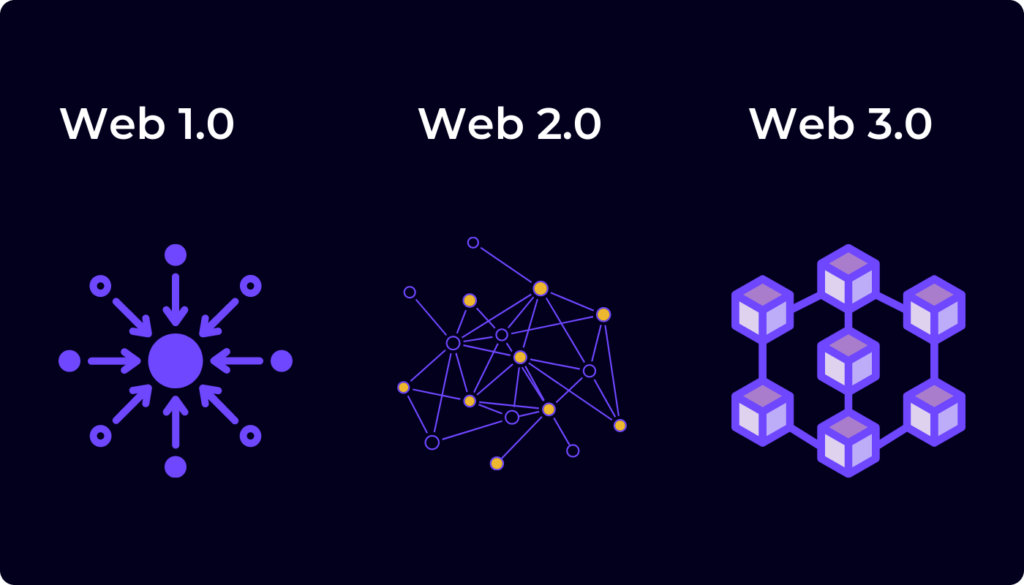
Web 1.0 (1990-2004), often called the “Read-Only” web, was the first internet generation. It was characterised by static web pages primarily used for reading information. Users could access information but had limited interaction with the content. Individuals or organisations with technical know-how created websites, and users were primarily content consumers.
Transitioning to Web 2.0 (2004-present), the “Read-Write” web marked a significant shift towards interactivity and user-generated content. This era introduced platforms like social media sites, blogs, and wikis, enabling users to consume, create, and share content. The web became more dynamic and collaborative but more centralised, with a few significant platforms controlling vast amounts of data.
We are now entering the era of Web 3.0, the “Read-Write-Own” web. This next phase is characterised by a return to the internet’s decentralised roots, powered by blockchain technology and Web3 protocols. In Web3, users can read, write, and truly own their data. It’s a vision of the internet where users have control over their data, identity, and digital assets. This shift towards decentralisation promises increased privacy, security, and user agency.
Understanding Web3 Protocols
Web3 protocols are the technical frameworks that form the foundation of the decentralised web, also known as Web3. These protocols are rules and procedures that dictate how nodes within a decentralised network communicate and interact. They are designed to support a broad range of activities, including secure data storage and retrieval, digital transactions, and the execution of smart contracts, all within a transparent and secure environment.
Web3 protocols are instrumental in powering the decentralised web by facilitating peer-to-peer interactions, eliminating the need for centralised intermediaries. This is a significant shift from the traditional Web2 model, which relies heavily on centralised servers and intermediaries. By removing these intermediaries, Web3 protocols pave the way for a more open, inclusive, and user-centric internet.
In the context of the decentralised web, Web3 protocols play a pivotal role. They enable the creation and operation of decentralised applications (DApps), foster interoperability between different blockchain networks, and provide the infrastructure necessary for a truly decentralised internet. By understanding Web3 protocols, we can gain a deeper insight into the mechanics of the decentralised web and appreciate its potential for transforming our digital lives.
Web3 Benefits
Interoperability: Interoperability is a significant advantage of Web3 protocols. It refers to the ability of different systems and applications to work together and share information seamlessly. In the context of Web3, interoperability means that various decentralised applications (DApps) and services built on the same protocol can interact without any barriers. This creates a more integrated and efficient web ecosystem, breaking down the silos that exist in the current Web2 model.
Security: Web3 protocols are often built on blockchain technology and are renowned for its robust security features. These protocols inherit the security benefits of the blockchain, such as immutability and transparency. Immutability ensures that once data is added to the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, providing a reliable and tamper-proof record of transactions. Transparency allows all network participants to view and verify transactions, making it extremely difficult for fraudulent activities to go unnoticed.
Privacy: Privacy is another key benefit of Web3 protocols. Unlike Web2, where large tech companies often control and monetise user data, Web3 gives users control over their data. Users can decide who can access their data and for what purpose, enhancing privacy and data sovereignty. Furthermore, many Web3 protocols incorporate advanced cryptographic techniques to secure user data, further enhancing privacy.
Key Web3 Technologies
1. Peer-to-Peer Networks: Peer-to-peer (P2P) networks are a fundamental part of Web3 technologies. In a P2P network, all participants, known as peers, interact directly with each other without the need for a central authority or server. Each peer makes a portion of their resources, such as processing power, disk storage, or network bandwidth, directly available to other network participants. This allows direct sharing of resources and information between devices or users without relying on a central server. The P2P model is a decentralised network architecture where each participant acts as a client and a server, enabling them to share resources and services directly with peers.
2. Decentralized File Storage: Decentralized file storage is another key component of Web3 technologies. Instead of storing data with a single cloud company, decentralised file storage protocols cut your data into tiny pieces and then store packets on pseudonymous computers (nodes) linked to a decentralised network. This means that files are protected by a network of many different stakeholders rather than a single company. Decentralised file storage distributes data into various chunks and stores it inside different peer-to-peer network nodes. This application of blockchain technology improves data security and privacy while serving as an alternative to centralised cloud storage.
3. Blockchain: Blockchain is a distributed ledger with growing lists of records (blocks) securely linked together via cryptographic hashes. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. Blockchain records are not unalterable; blockchains may be considered secure by design and exemplify a distributed computing system with high Byzantine fault tolerance since blockchain forks are possible. Blockchain technology forms the backbone of many Web3 applications, including cryptocurrencies and decentralised applications (DApps).
4. Other Web3 Technologies: Besides the above, several other technologies play a crucial role in the Web3 ecosystem. These include smart contracts, decentralised autonomous organisations (DAOs), decentralised exchanges (DEXs), and more. These technologies leverage the principles of decentralisation, transparency, and immutability offered by blockchain technology to create a more open and equitable digital world. They pave the way for a more transparent, inclusive, and user-centric internet.
The Role of Web3 Protocols in Decentralized Applications (DApps)
Web3 protocols are instrumental in the functioning of Decentralized Applications (DApps). DApps are applications that run on a blockchain or a peer-to-peer network of computers rather than on a centralised server. Their users collectively control them, a significant shift from traditional applications.
Web3 protocols provide the infrastructure for DApps. They set the rules for how nodes in the network communicate and share data, enabling direct interactions between peers without a central authority. This is the essence of decentralisation, and it’s what makes DApps possible.
For example, DApps often use smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement written into code. These smart contracts interact with blockchains like Ethereum, and Web3 protocols govern their execution.
Furthermore, Web3 protocols enable DApps to interact with each other, creating a more integrated and efficient web ecosystem. This interoperability allows various DApps and services built on the same protocol to work together seamlessly. Stay tuned with Latest Web3 News for more interesting info like this!
